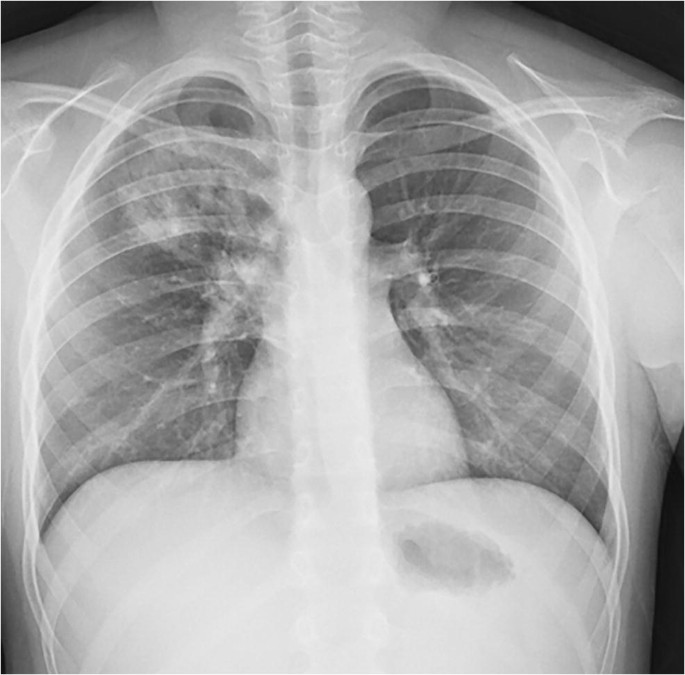
Left Basilar Airspace Disease
Left basilar airspace disease. This condition causes problems in. Air space opacification is a descriptive term that refers to filling of the pulmonary tree with material that attenuates x-rays more than the surrounding lung parenchyma. Left basilar airspace disease Vertebral basilar insufficiency children Basilar-type migraine disease.
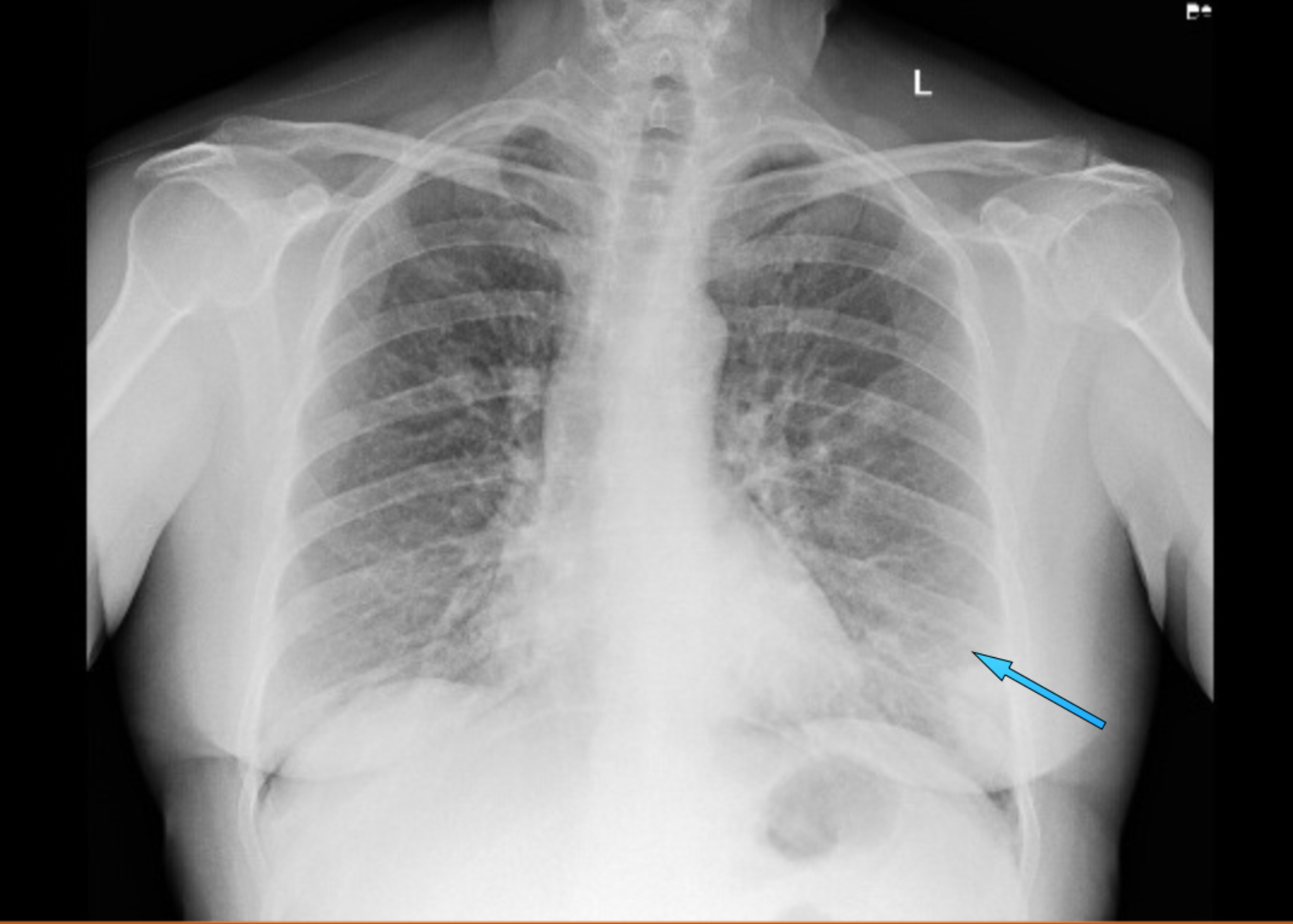
Causes of acute alveolar lung disease include pulmonary edema cardiogenic or neurogenic pneumonia bacterial or viral systemic lupus erythematosus bleeding in the lungs eg Goodpasture syndrome idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Persistent right basilar airspace disease with increasing left upper lung airspace disease. When you have an infection in your lung your body sends white blood cells to fight it.
J984 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Pneumothorax is the presence of air between the lung and the chest wall which can cause the lung to collapse. Andrew Murphy and Assoc Prof Frank Gaillard et al.
It occurs when tiny air sacs in the lungs known as alveoli deflate. It is common during asbestosisa lung disease caused by the inhalation of asbestos particles. Any pathological process that displaces air from the alveoli will be depicted as airspace opacification but this pattern is most commonly seen when either fluid accumulates as in pulmonary oedema or there are inflammatory cells as with infection in the airspaces.
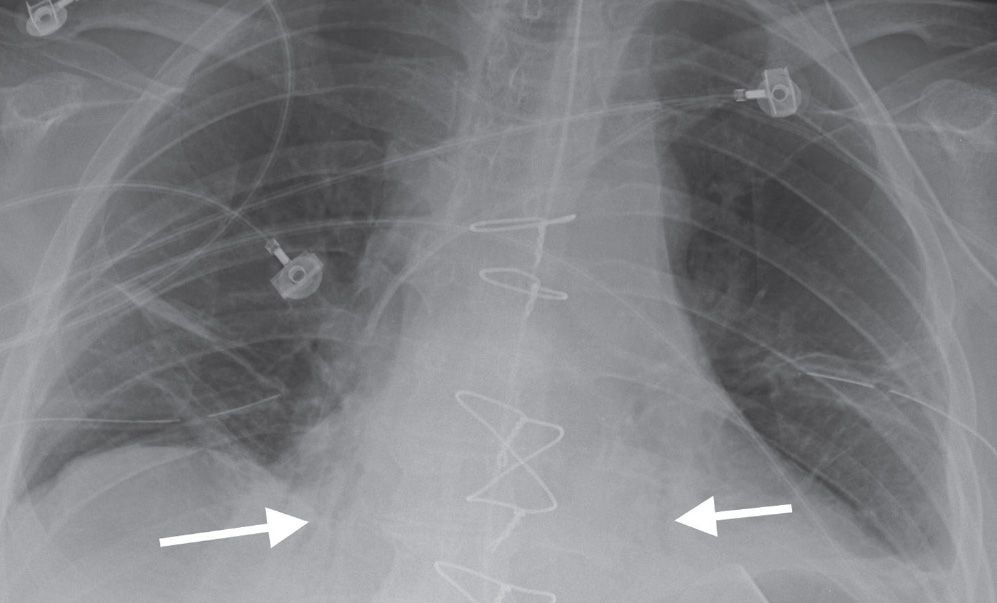
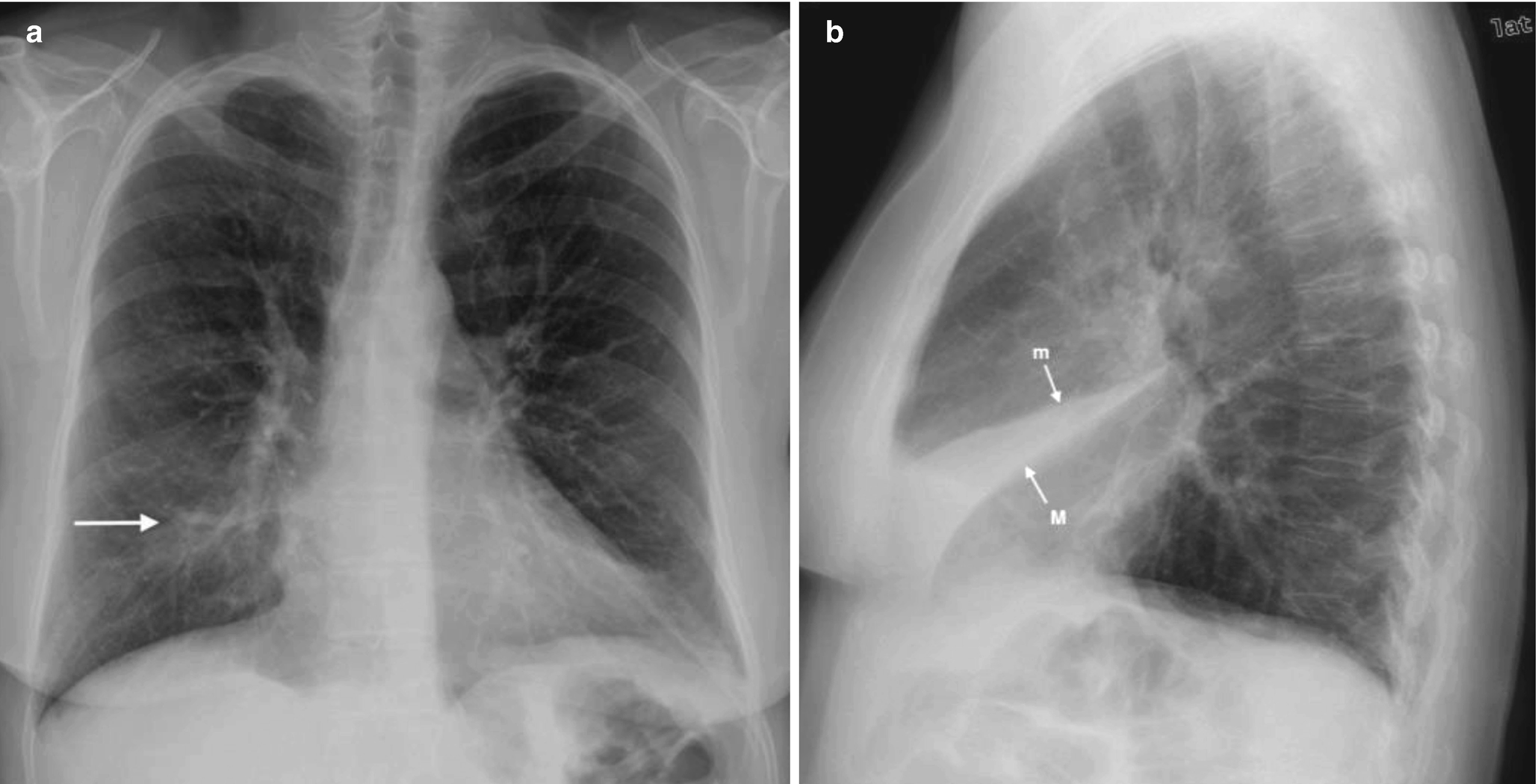
It is one of the many patterns of lung opacification and is equivalent to the pathological. Basilar atelectasis or simply atelectasis is the collapse of either the entire or part of the lung due to some obstruction or blockage. Bibasilar airspace disease can be diagnosed through a chest X-ray.
Airspace refers to the alveoli which are air sacs that aid in oxygen exchange. Increasing patchy multifocal airspace disease. The major airways are made narrower by disease.
Basilar atelectasis is the name offered to the condition where either a part of the lung or the whole lung collapses due to a barrier. The particular way the lung collapses can often produce a.
Pneumonia is the most common cause of lung consolidation.
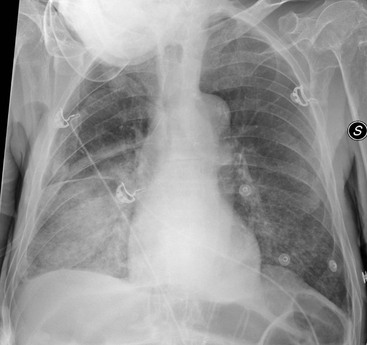
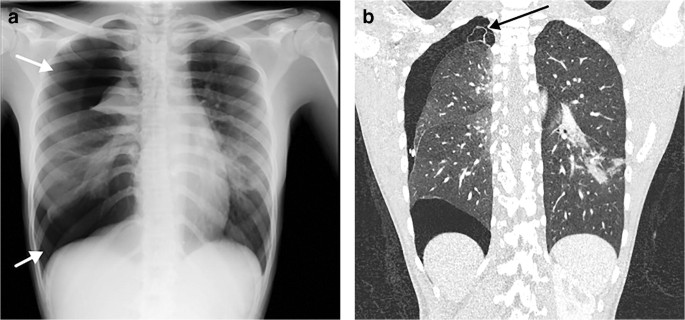
Causes of acute alveolar lung disease include pulmonary edema cardiogenic or neurogenic pneumonia bacterial or viral systemic lupus erythematosus bleeding in the lungs eg Goodpasture syndrome idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. CT scanning showed basilar-predominant airspace disease with areas of ground-glass opacifi cation consolidation and air bronchograms. Basilar atelectasis is the name offered to the condition where either a part of the lung or the whole lung collapses due to a barrier. Its definition is derived from. Andrew Murphy and Assoc Prof Frank Gaillard et al. Bibasilar airspace disease can be diagnosed through a chest X-ray. This condition causes problems in. This unusual type of bibasilar atelectasis happens when the lung is trapped as a result of pleural disease while being devoid of air. Air space opacification is a descriptive term that refers to filling of the pulmonary tree with material that attenuates x-rays more than the surrounding lung parenchyma.
Less common causes include bleeding or protein secretions within the lungs. J984 is a billablespecific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. This appears to be consistent with other reported cases of AFOP 13 in which the most common pattern is bilat- eral basilar airspace disease. Alveolar lung disease may be divided into acute or chronic. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J984 - other international versions of. Pneumothorax is the presence of air between the lung and the chest wall which can cause the lung to collapse. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM J984 became effective on October 1 2020.




























Post a Comment for "Left Basilar Airspace Disease"