Celiac Disease Hla Dq Assoc
Celiac disease hla dq assoc. More than 95 of celiac disease patients are positive for DQ2 half DQ2 or DQ8 but many individuals with these genetic results do not develop celiac disease. Gluten peptides presented by these HLA molecules induce. No significant association was found between DQ22 variant and celiac disease in the studied population.
Study of the HLA associations in patients not carrying these heterodimers has been limited by the rarity of such pa-tients. This European collaboration has provided a unique. Background Information for Celiac Disease HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 Genotyping.
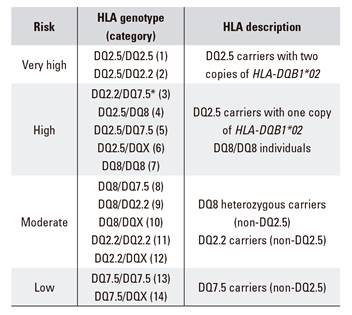
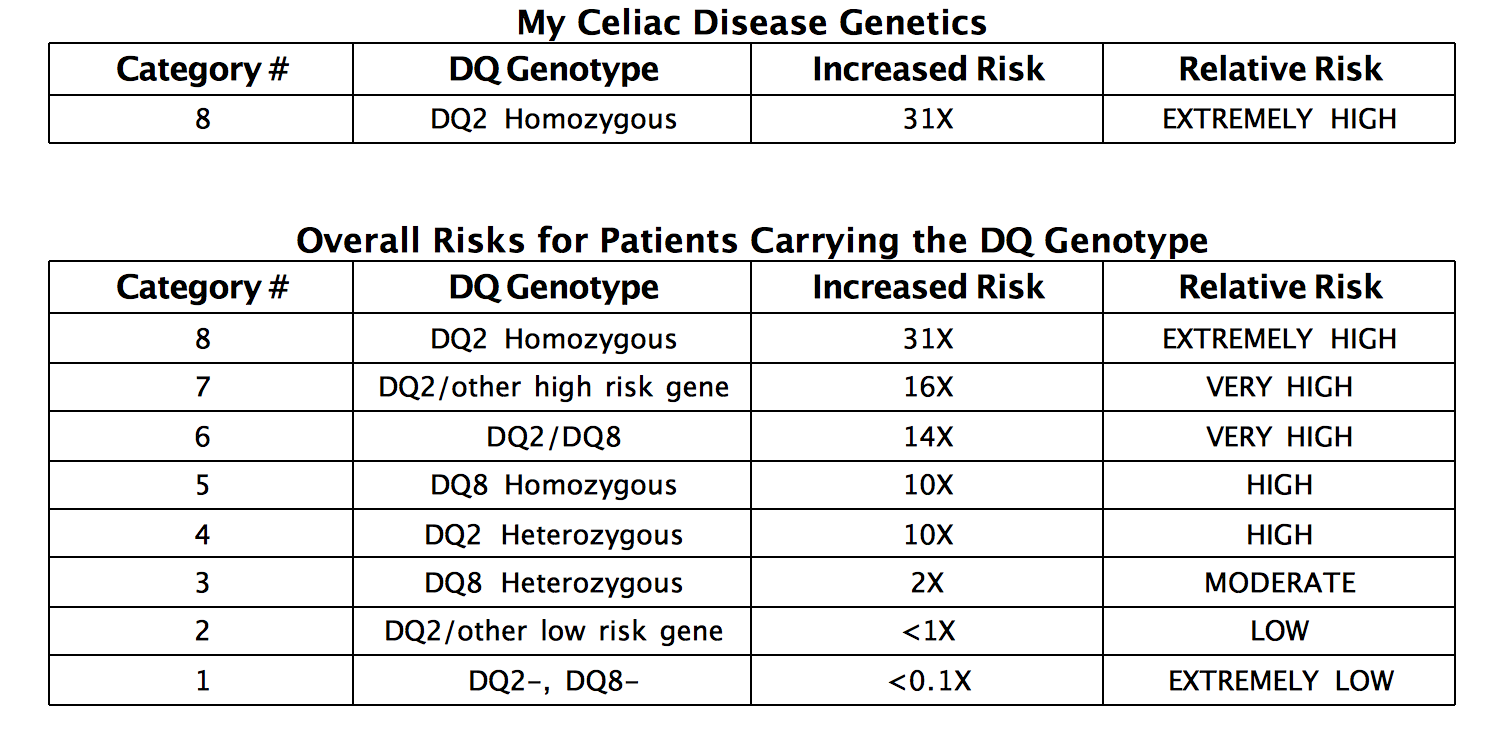
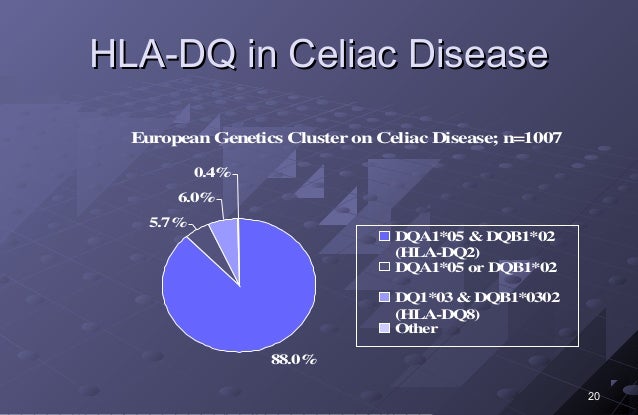
The genotyping of celiac disease HLA-DQ predisposing alleles showed similarities with both European and non-European patterns which may be a reflection of the miscegenation that originated the actual Brazilian population. Most 90-95 patients with celiac disease have 1 or 2 copies of HLA-DQ2 haplotype see below while the remainder have HLA-DQ8 haplotype. The absence of these haplotypes excludes a diagnosis of CeD.
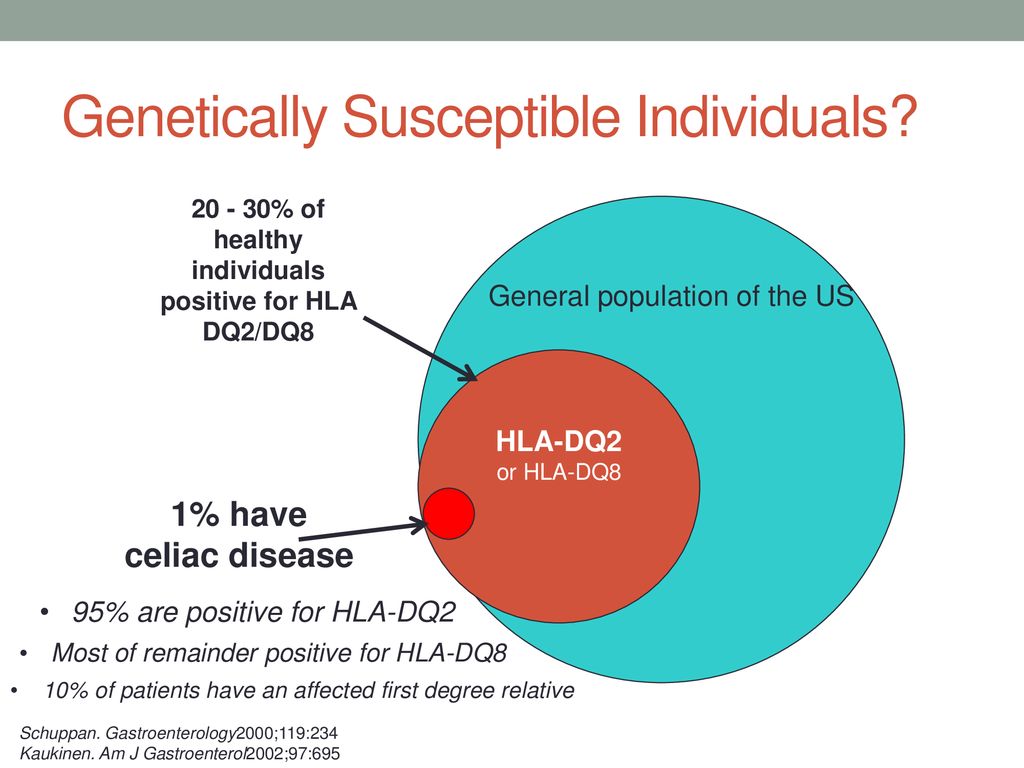
HLA-DQ typing in the diagnosis of celiac disease. An absence of celiac disease-associated alleles reduces the lifetime risk of developing celiac disease to well below 004 independent of diet. More than 95 of celiac disease patients are positive for DQ2 half DQ2 or DQ8 but many individuals with these genetic results do not develop celiac disease.
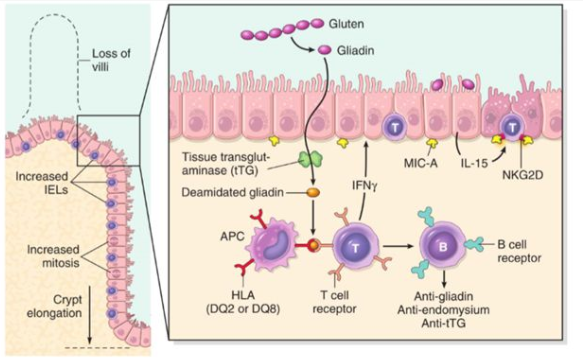
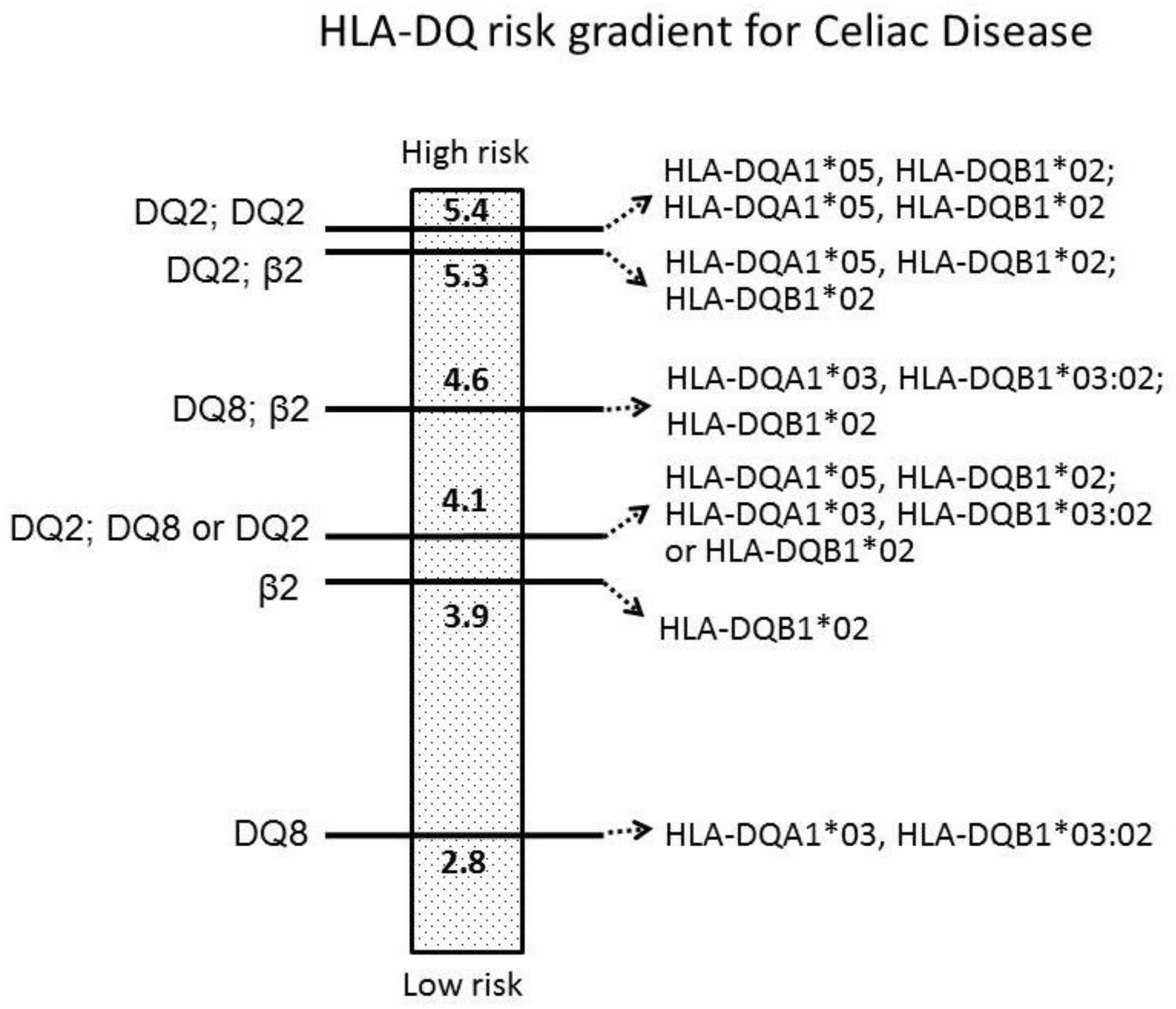
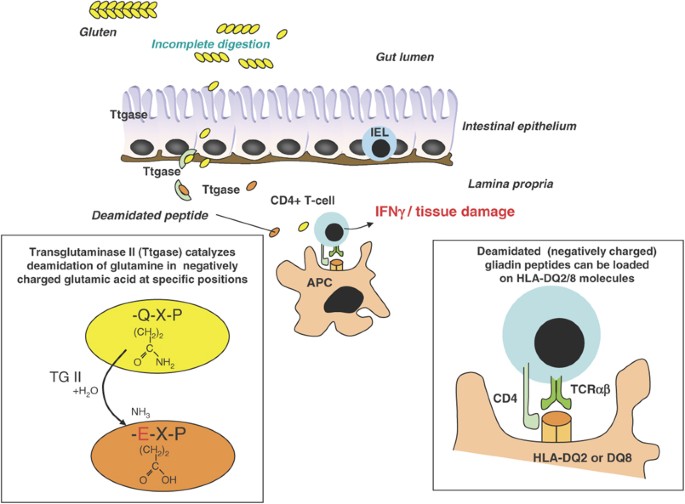
Genetic susceptibility to celiac disease is strongly associated with HLA-DQA105-DQB102 DQ2 and HLA-DQA103-DQB10302 DQ8. HLA-DQ2 is found in more than 90 of celiac cases HLA-DQ8 in 5 and half DQ2 in almost all remaining cases1 A negative HLA-DQADQB test result essentially excludes celiac disease as a diagnosis14 Although a. Celiac disease is strongly associated with the HLA genetic region.
In 1 study of celiac disease only 07 of patients with celiac disease lacked the HLA alleles mentioned above. Has a multifactorial cause and depends on genetic immunological and environmental factors for its development. Rare exceptions to these associations have been occasionally seen.
Sequence Based Typing SBT andor Sequence Specific Primers SSP may be used as supplemental methods when necessary. 1celiac disease Celiac Disease Genetic Testing HLA-DQADQB genetic testing is an important tool in evaluating patients for celiac disease.
Celiac Disease HLA DQ Assoc.
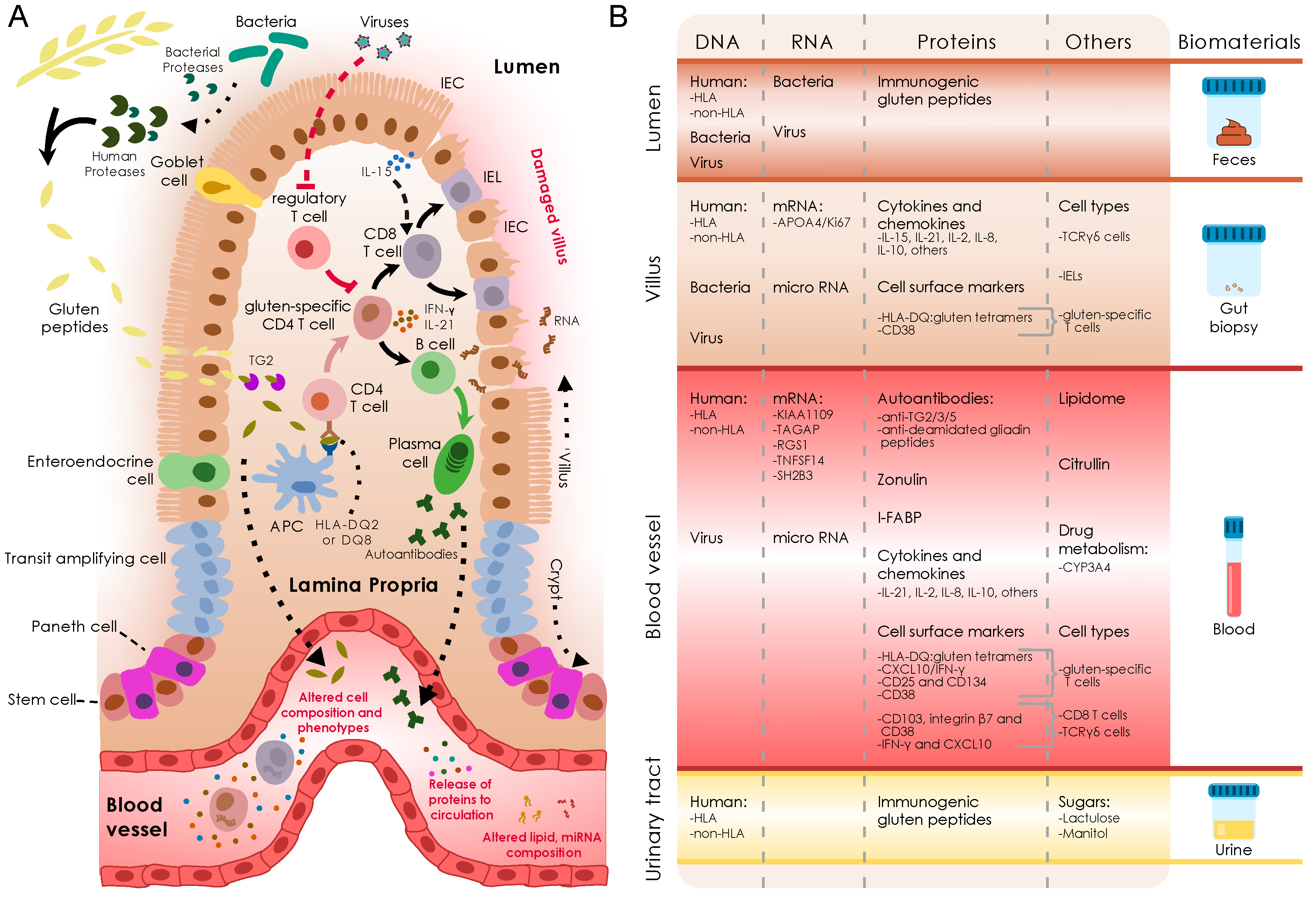
Has a multifactorial cause and depends on genetic immunological and environmental factors for its development. In 1 study of celiac disease only 07 of patients with celiac disease lacked the HLA alleles mentioned above. This European collaboration has provided a unique. The low specificity of this test must however be borne in mind. 1celiac disease Celiac Disease Genetic Testing HLA-DQADQB genetic testing is an important tool in evaluating patients for celiac disease. Diarrhea weight loss anorexia lactose intolerance and abdominal distention and discomfort. In 1 study of celiac disease only 07 of patients with celiac disease lacked the HLA alleles mentioned above. Celiac disease is an enteropathy characterized by gluten sensitivity and broad clinical aspect. Patients with celiac disease CeD carry the major histocompatibility complex class II HLA-DQ2 or DQ8 haplotype.
Most of the DQ2 negative patients express the HLA-DQ8 molecule. Aids in the diagnosis of celiac disease. Most 90-95 patients with celiac disease have 1 or 2 copies of HLA-DQ2 haplotype see below while the remainder have HLA-DQ8 haplotype. Genetic susceptibility to celiac disease is strongly associated with HLA-DQA105-DQB102 DQ2 and HLA-DQA103-DQB10302 DQ8. Limitations The HLA DQ Association test detects celiac disease-associated alleles that predispose to the disorder but is not diagnostic of celiac disease. The HLA DQ Association test provides genotyping for detection of. Approximately 90 of celiac patients express the HLA-DQ2 molecule.






































Post a Comment for "Celiac Disease Hla Dq Assoc"